Research
Google Scholar - Complete list of the lab’s publications.
Open Datasets - Access our open-source datasets and request data for your research.
Computational Neuroscience
Computational neuroscience offers a new way to understand the brain by leveraging advances in computing, artificial intelligence, applied mathematics, statistics and biophysics. The lab’s research in computational neuroscience focuses on:
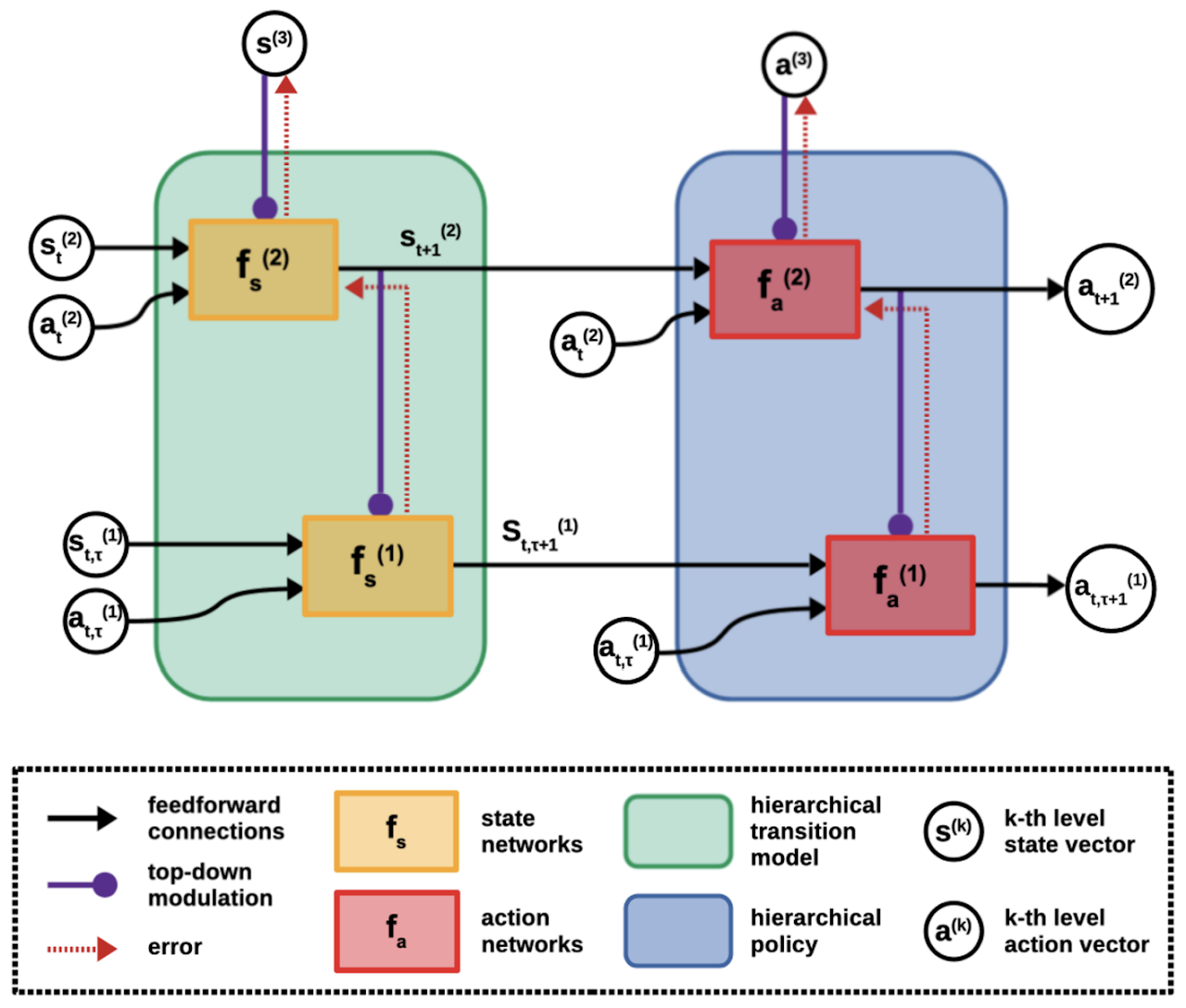
- Predictive coding and Bayesian brain models
- Models for ehavior and cognition based on partially observable Markov decision processes (POMDPs)
- Hierarchical recurrent neural networks implementing the above models
Brain-Computer Interfaces
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) are devices that connect brains directly to computers. BCIs can both record from the brain (“read” the brain) and stimulate the brain (“write” the brain). BCIs be used to help those who have impairments due to injury or neurological conditions. For example, by recording electrical signals from the brain, a BCI (1) can decode these signals into intention, such as the intention to move, and (2) actuate this intention by performing some output, such as moving a prosthetic arm, or turning on a light. Our lab works closely with neuroscientists, neurosurgeons and patients to explore novel methods to improve BCI technology. Current research projects include:
- Brain co-processors: This project utilizes artificial intelligence to adaptively deliver stimulation and compute control signals as a function of the brain’s ongoing neural activity and external sensory signals.
- Naturalistic BCIs: This project uses deep learning methods to improve decoding of brain signals in naturalistic settings.
- Decoding pain and mood: This project seeks to identify neural biomarkers for pain and mood.
- Modeling electrical stimulation: This project models the effects of therapeutic electrical stimulation using AI and machine learning techniques, and uses these models for developing brain co-processors.
Artificial Intelligence and Reinforcement Learning
Our lab focuses on developing neurally inspired AI algorithms that leverage insights from computational models of the brain. We aim to design AI systems that are more adaptive, interpretable, and capable of solving complex real-world problems. Our recent research includes:
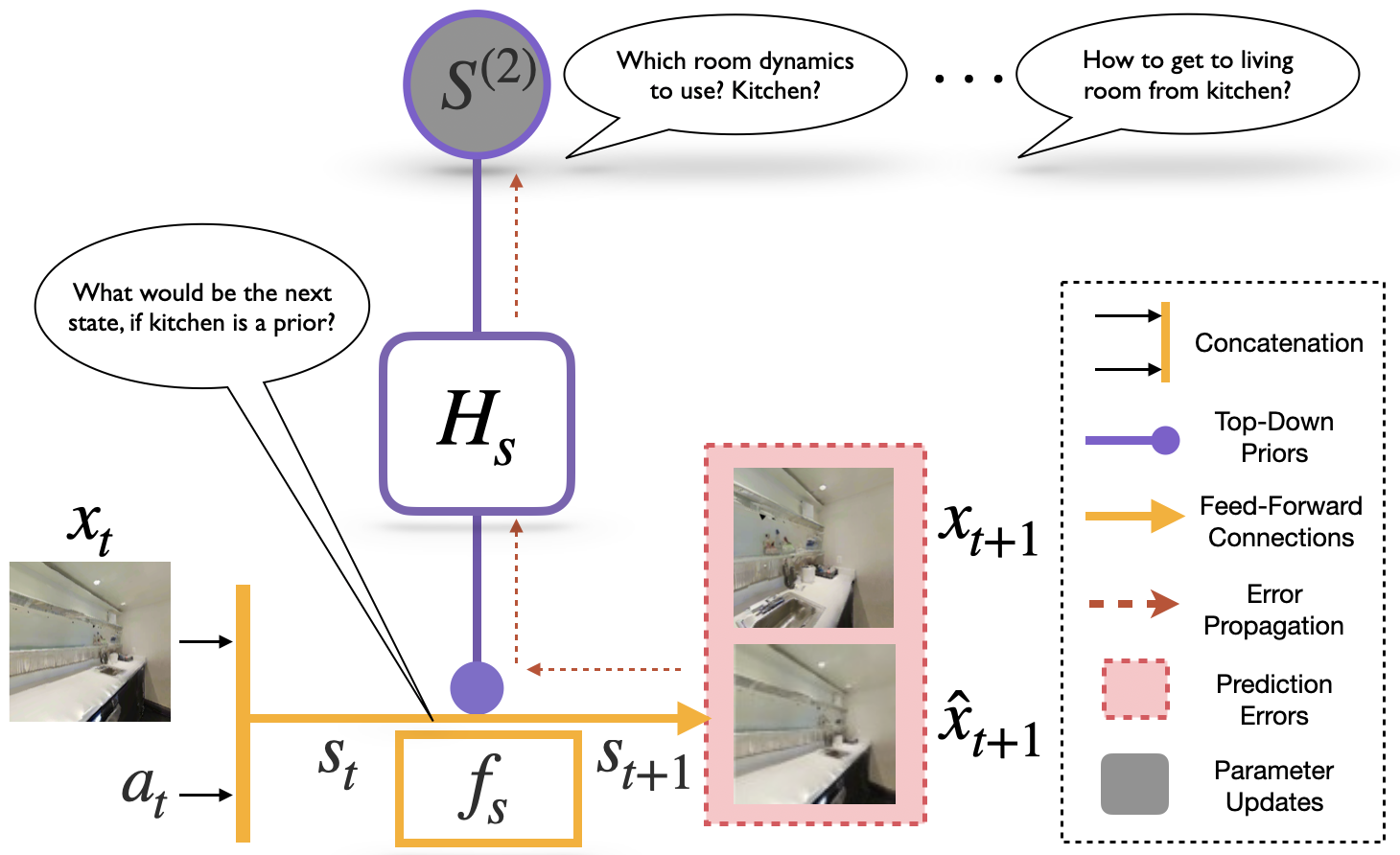
- Active Predictive Coding: Developing dynamic, hierarchical world models that learn to compose simple dynamics, enabling AI to tackle complex tasks in vision and navigation.
- Visual Reinforcement Learning for Grounded Decision-Making: Investigating how reinforcement learning (RL) agents perceive and interpret their environments when making decisions.
- Active Inference and Successor Representations for Navigation: Integrating active inference with successor representations to create more flexible and efficient navigation strategies.
- Using AI to analyze the Indus script and art